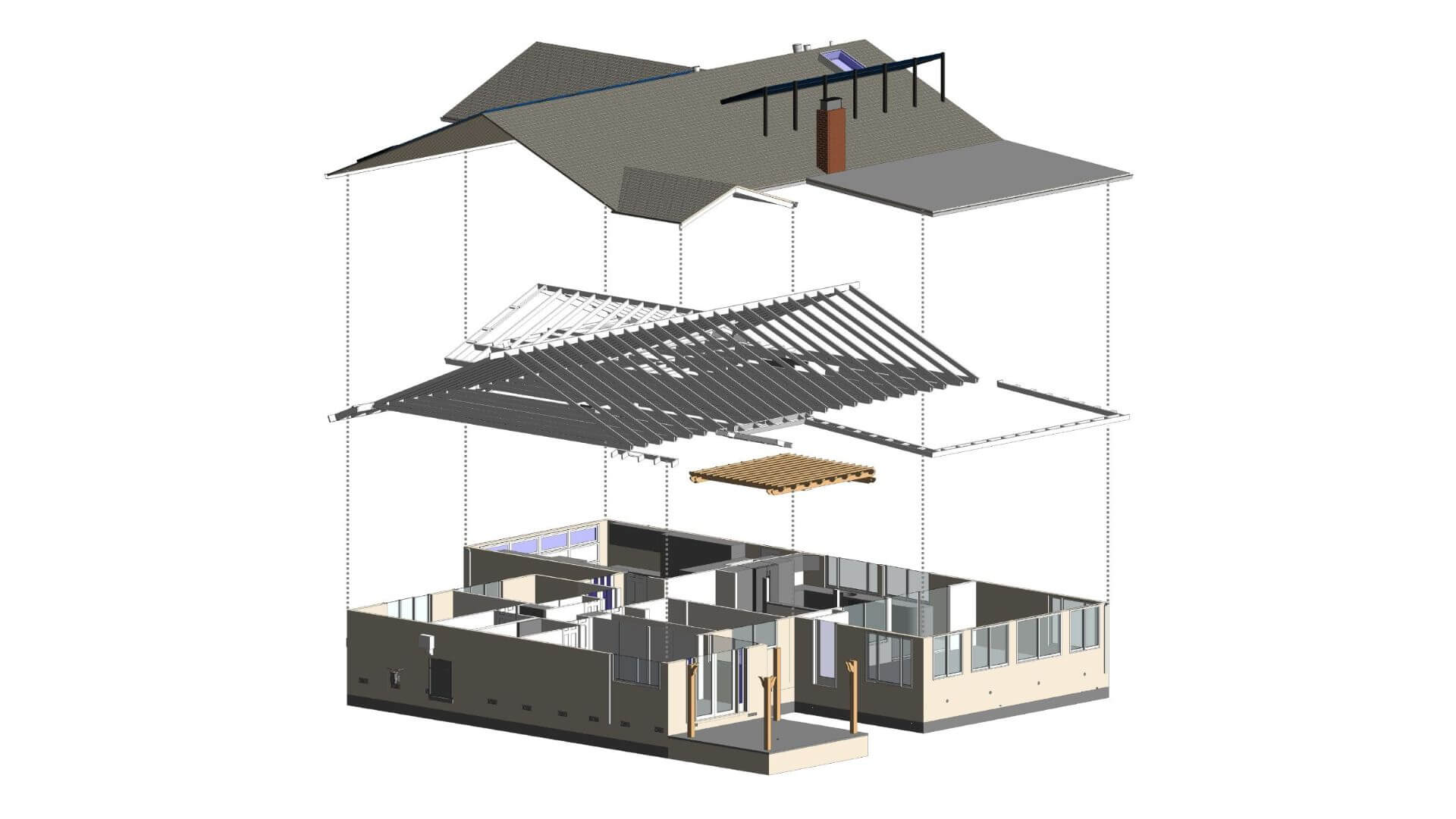
In the nowaday’s reality of architecture, the ability to envision and conceptualize designs is incredibly significant. Yet, translating these visions into tangible, feasible structures often poses significant challenges. This is where 3D modeling emerges as a transformative tool, revolutionizing the way architects bring their ideas to life. But what exactly is 3D modeling in architecture, and why has it become an unparalleled asset in the modern architect's toolkit?
In this article, we dive into the intricacies of 3D modeling within the architectural sphere, offering insights into its profound impact on the design process.
Looking for professional architectural 3d modeling services? Contact us at Alterpex.
Definition of 3D Modeling in Architecture
At its core, 3D modeling in architecture is the process of generating three-dimensional representations of architectural designs using specialized software. It transcends the limitations of conventional two-dimensional drawings by constructing virtual models that mimic real-world structures in detail. These models replicate dimensions, material properties, and aesthetic elements of architectural projects, providing a comprehensive visual insight into their form and function.
3D modeling allows architects to create detailed visual representations of their designs, providing a better understanding of the project. It helps clients visualize the outcome, leading to improved communication and fewer misunderstandings. By using 3D models, architects can identify design flaws early on, saving time and resources during the construction phase.
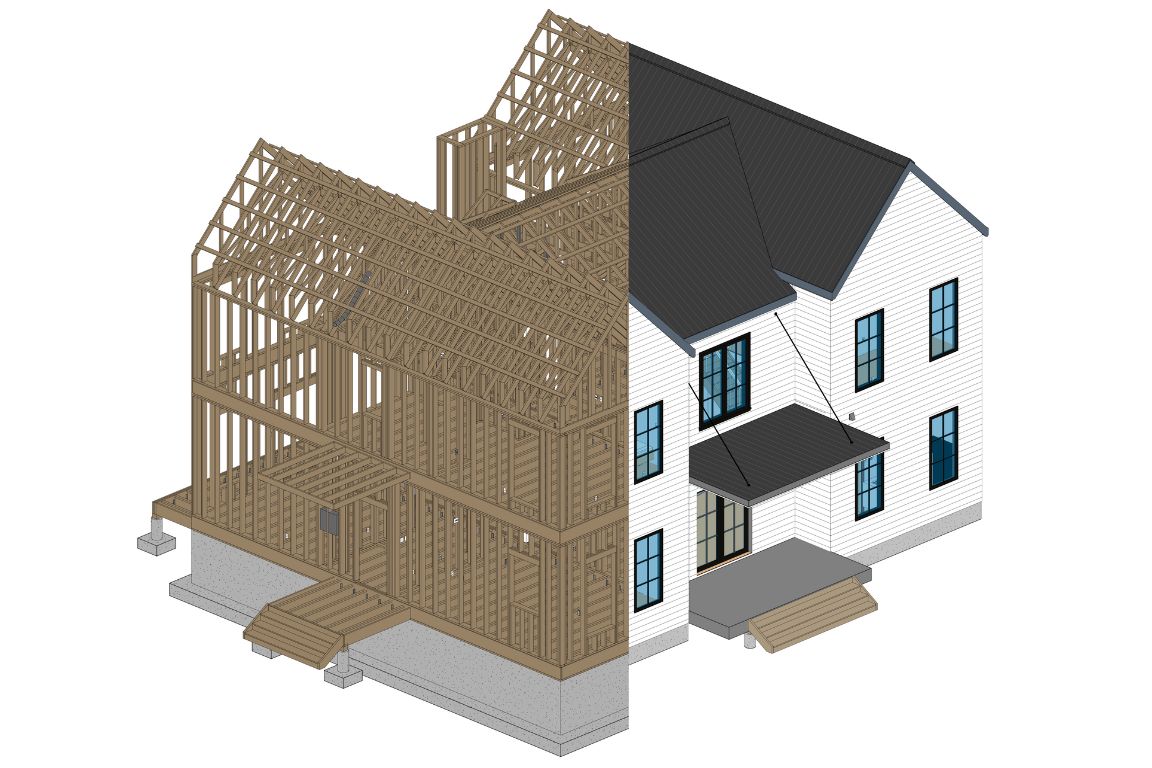
Benefits of 3D Modeling in Construction and Architecture
Let's look into the several benefits it brings to the table:
1. Enhanced Visualization and Spatial Understanding: 3D modeling empowers architects and stakeholders to transcend the limitations of traditional 2D drawings and envision designs in three dimensions.
2. Improved Communication and Collaboration. With 3D models, architects can effortlessly convey their vision to clients, contractors, and team members. These lifelike representations facilitate clear, concise communication, minimizing misunderstandings and ensuring alignment across all stakeholders.
3. Increased Efficiency in Design and Scheduling. 3D modeling utilises new technologies ranging from 3D scanners and printers to artificial intelligence which streamlines the design process, allowing architects to explore multiple concepts rapidly and refine them with ease. With the ability to create 3D models of commercial buildings and visualize the impact of design changes in real time, architects can make informed decisions swiftly, accelerating the project timeline without compromising the quality.
4. Cost Savings and Error Reduction. 3D modeling eliminates the risk of errors by providing a comprehensive overview of the project before construction commences. By identifying and rectifying potential issues during the design phase, architects can minimize rework, optimize material usage, and ultimately save costs while delivering a project on time.
Difference between 2D and 3D Modeling
In architecture, 2D drafting involves creating flat representations of structures, like floor plans or elevations. On the other hand, 3D modeling brings projects to life by adding depth and perspective. Unlike 2D plans, which can be limiting in visualizing a project, 3D models offer a comprehensive view from various angles.
When architects use 2D drawings, they might struggle to get enough information. However, with 3D modeling, clients can better understand the final look of a building before construction even begins. This technology allows for more accurate planning and design adjustments as needed.
Types of 3D modeling
1. Direct modeling is a type of 3D modeling approach where designers directly manipulate the geometry of the model without being constrained by its construction history. One of the key advantages of direct modeling is its simplicity and ease of use. In direct modeling, changes are made directly to the 3D geometry, such as moving, rotating, scaling, or deleting individual faces, edges, or vertices.
2. Building Information Modeling (BIM) is a digital representation of the physical and functional characteristics of places. BIM models are intelligent, 3D digital representations of buildings and infrastructure that provide architects, engineers, contractors, and other stakeholders with a comprehensive understanding of a project. BIM modeling goes beyond traditional 3D modeling by incorporating additional layers of data and information associated with the various components of a building or structure. This technology provides numerous benefits to the construction and architecture industries, including improved collaboration, reduced errors and rework, and enhanced project efficiency and sustainability.
3. Spline modeling is a technique used in computer graphics and 3D modeling to create smooth and organic shapes by defining curves known as splines. Splines are mathematical representations of smooth curves that are defined by a series of control points or vertices. These control points can be manipulated to adjust the shape and curvature of the spline, allowing for precise control over the final form of the model. One of the key advantages of spline modeling is its ability to create complex and organic shapes with smooth, continuous surfaces.
4. Point cloud modeling also known as Scan-to-BIM is a technique used in 3D computer graphics and modeling where a large set of points in three-dimensional space is used to represent the structure or environment. These points are typically captured by using various scanning technologies such as LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) or photogrammetry. In point cloud modeling, each point in the dataset contains information about its position in 3D space, as well as potentially additional attributes such as color or intensity. By processing and analyzing these points, it is possible to reconstruct a detailed and accurate 3D model of the scanned object or environment. One of the key advantages of point cloud modeling is its ability to capture detailed geometric information about complex surfaces and structures with a high level of accuracy.
5. Polygonal modeling is a widely used technique in 3D computer graphics and modeling where objects are constructed using geometric primitives called polygons. These polygons, typically triangles or quads, are arranged and connected to form the surface of the object. In polygonal modeling, the surface of the object is represented by a mesh composed of interconnected polygons. Each polygon has vertices, which are points in three-dimensional space, and edges, which connect the vertices. By manipulating the positions of the vertices and adjusting the connectivity of the polygons, artists can create a wide variety of shapes and structures. One of the key advantages of polygonal modeling is its versatility and efficiency. Additionally, polygonal models can be easily textured, animated, and rendered using standard computer graphics techniques. While polygonal modeling is highly flexible and powerful, it also has some limitations. For example, polygonal models may not always accurately represent smooth or organic shapes, leading to visible faceting or jagged edges. Additionally, creating highly detailed models with a large number of polygons can be computationally intensive and may require specialized techniques such as subdivision surface modeling or sculpting.

Popular Software Programs for 3D Modeling
1. Autodesk Revit offers comprehensive features tailored specifically for architectural design projects, construction, BIM models, and scheduling.
2. SketchUp's user-friendly interface makes it a favorite among beginners and professionals alike due to its versatility in creating intricate models swiftly.
3. Other widely used programs include Rhino 3D known for its flexibility in handling complex geometries effectively.
4. AutoCAD is an older uncle of Autodesk Revit that recently updated its capabilities to create and manipulate 3D models as well, even though it used to be largely known for 2D drafting.
Selecting the appropriate software is crucial in architecture as it significantly impacts workflow efficiency and project outcomes. When considering which software to use, architects should evaluate factors such as ease of use, compatibility with other tools, available features/extensions, the learning curve involved, and overall cost.
Process of 3D Modeling for Construction
Creating a 3D model for construction involves several steps. First, architects start by gathering data such as measurements and images. Then, they use specialized software to model the structure in three dimensions accurately. This process includes adding textures, colors, and details to make the model realistic. Next, they refine the model based on feedback from clients or team members before finalizing it for presentations or further development.
Pros:
Improved visualization of the project.
Enhanced communication with stakeholders.
Complex Data for all parties on the project.
Cons:
Requires specialized skills and software expertise.
You've now journeyed through the most important aspects of 3D modeling in architecture. As you grasp the technical intricacies and creative possibilities within this field, remember that each pixel crafted by a 3D artist holds the potential to shape limitless ideas.
Author:
Yuriy Alex Kulchytsky
Head of VDC Services from Alterpex
1027 Wilshire Blvd, Suite 844, Los Angeles, California 90017
alterpex.com
Email: info@alterpex.com
Phone: (415) 696-4180